Queensland Aphasia Research Centre (QARC)
Optimising the lives of people with Aphasia
CHAT-Maintain
CHAT-Maintain is a home therapy program. It uses technology to do therapy at home.
The aim of this project was to see whether CHAT-Maintain helped people to keep up therapy gains after intensive aphasia therapy.

Key outcomes of this research
CHAT-Maintain may help to keep up therapy gains after intensive therapy.
We need to think about better ways to support quality of life.
Background
There is evidence that aphasia therapy works.
But therapy gains may not last for a long time.
CHAT-Maintain uses technology to practice aphasia therapy at home.
What did the research involve?
CHAT-Maintain was offered to people with aphasia.
CHAT-Maintain was given after intensive therapy (CHAT or TeleCHAT).

We made a home therapy plan with the person with aphasia.
We gave training on how to use technology.
People with aphasia practiced therapy at home for 6 months.
We made support phone calls once a month.
Who did the research?
22 people with aphasia consented to CHAT-Maintain.
16 people finished CHAT-Maintain.
People with aphasia did about 40 hours of home practice over 6 months.
Some people with aphasia needed support to use the technology.
Some people with aphasia needed extra equipment to practice at home.
What did the researchers find?
Therapy gains were kept up 3 months after therapy.
Some therapy gains were kept up 6 months after therapy.
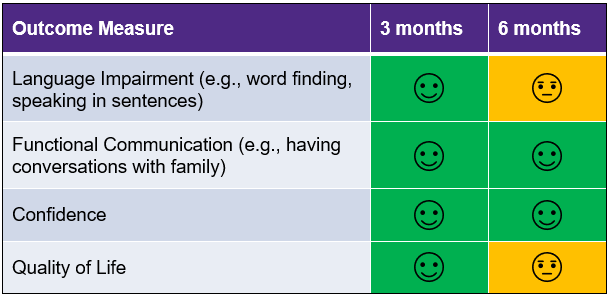
![]()
Therapy gains kept up.
![]()
Therapy gains not kept up.
![]()
Therapy gains greater than pre-test but less than post-test.
What's next?
These results will be presented at conferences.
The results will be published in a journal article.
Contact
If you have any questions about CHAT-Maintain you can contact QARC:
This research was funded by the Stroke Foundation.
We acknowledge Dr Jessica Campbell’s valuable contribution to this research.

